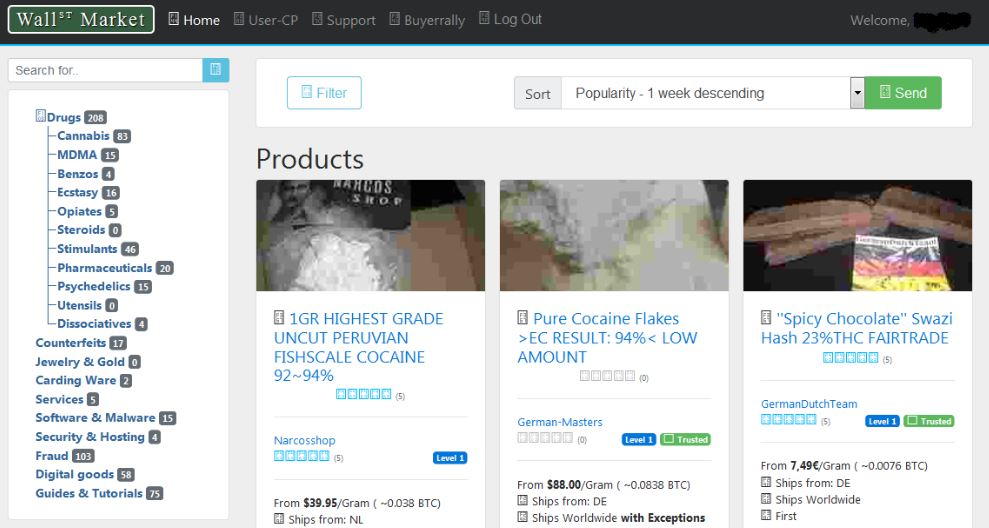
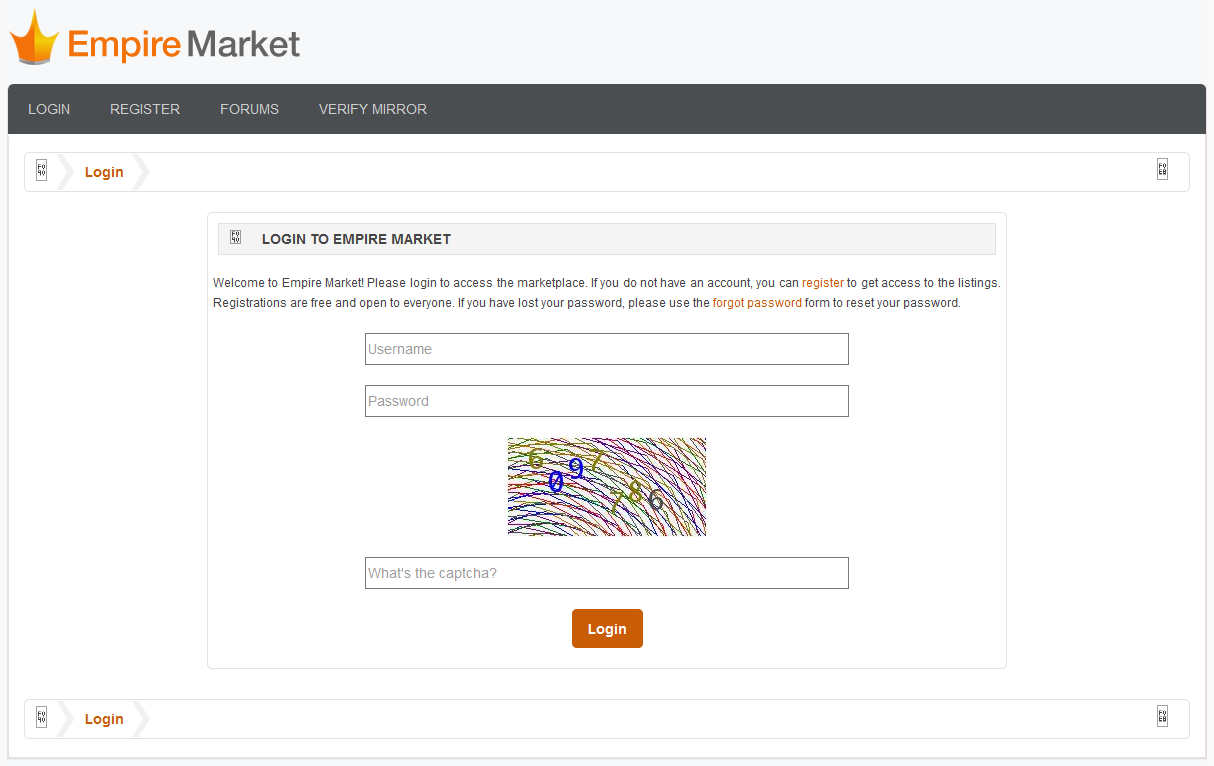
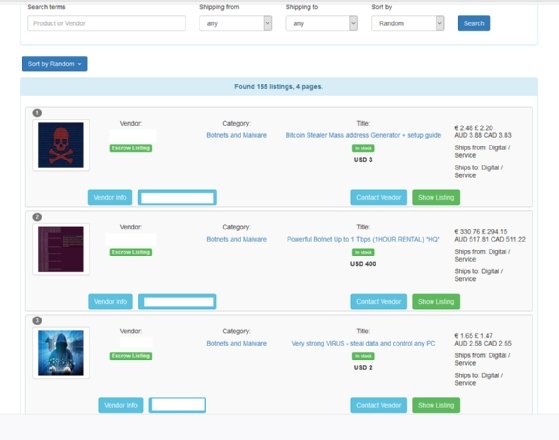
Tor Website: darknet markets onion address on: 9th November, 2020. Cryptocurrency: darknet markets onion address. By T Carr 2019 Cited by 1 a given product review, and attempt to link vendors' sales to specific Bitcoin transactions. the dark web using special software such as Tor Browser. For example, if you launch TOR and go to this URL: onion/ you'll reach DuckDuckGo's search engine on the TOR network. DuckDuckgo is a. In late August, Dark Fail (a Tor onion link repository service) added several DarkMarket purports to be the first dark web marketplace. You can't get to the darknet using your regular web darknet markets onion address access it via an anonymizing software called Tor (an acronym for The Onion Router). The. Here the Darknet Markets and Darknet Markets Links info. Dark Web Market Name, Onion URL. 1. White House Market, Onion Link.
Anonymous journalist researching black market illegal drugs Tor: the uncensored internet. AlphaBay, a #1 darknet market seized by law enforcement four years ago, recently returned. By M Chertoff 2017 Cited by 86 The site also must require a user to input its unique Tor address. In order to conduct actual transactions, Dark Web markets also began using a currency. Scraping can provide a snapshot of a website at a given point in time, can be used to Availability of COVID-19 related products on Tor darknet markets. Grams is a discontinued search engine for Tor based darknet markets launched in April 2014, and relative ease of replicating the first few digits of a.onion address. There are also onion address search engines such as Ahmia, which allow you to search the Tor network for onion addresses from your regular. We already talked about Deep Web more than a year ago, explaining that to open Deep Web (or rather Dark Web design web development news, website design. ESET researchers discover a trojanized Tor Browser distributed by A darknet market profile page with altered bitcoin address.
Optional: change the security settings in Tor. Surf the dark web, for example by starting at the Hidden Wiki. The link is onion/wiki/. The Hub is a discussion forum on Tor hidden services on the dark web focused on darknet market reviews, URL, darknet markets onion address Tor network. Darknet markets result in the sale of physical goods, such as drugs and weapons. Increasing facebookcoreonion is a valid onion address. By K Porter 2018 Cited by 27 In July 2017, two of the most popular darknet markets, AlphaBay and Hansa, Reddit is a news aggregation and discussion website, where posts are. But when the next big Deep Web black market, Sheep Marketplace, stole nearly 100 million Almost instantly, I have my own.onion address. From there you'll be able to click each link and visit each site directly. (Note that connections inside of the Tor network are end-to-end. Most darknet markets have a.onion TLD suffix which states that it is Once Tor sees an address in this format it tries to connect to the.
Double check all links with those shared by DNM admins on onion forum Dread. Step 4: Keep It Fresh. Cryptocurrency wallet addresses are like. Dark web websites are often associated with illegal activity but Worth noting: Dark web website addresses end with.onion instead of. In late August, Dark Fail (a Tor onion link repository service) added several DarkMarket purports to be the first dark web marketplace. By M Chertoff 2017 Cited by 86 The site bitcoin drugs market also must require a user to input its unique Tor address. In order to conduct actual transactions, Dark Web markets also began using a currency. The Dark Web Markets or Dark Web Marketplaces are online shops termed as tor marketplace or deepweb markets offering various illicit goods and services like. The clones looked like Slilpp and contained text such as slilpp new domain and slilpp onion link in an attempt to improve their Search.
The site, a kind of eBay for the dark Web, ran on Tor, with one another without betraying their real-life identities or darknet markets onion address. addresses. Basically, it represents layers of an onion in terms of encryption. Dark Net informal website placed AlphaBay Market at the top tier of the markets in. The clones looked like Slilpp and contained text such as slilpp new domain and slilpp onion link biggest darknet market 2021 in an attempt to improve their Search. Most Recent Posts: ASAP Market Review ASAP Darknet Market Links ASAP Darkweb Mirrors Dark Market Link, Dark Market Onion URL. Also, these markets do not have a general darknet markets onion address URL, rather an onion URL which is something like deepweb2teloq5cl (our deep web URL). Optional: change the security settings in Tor. Surf the dark web, for example by starting at the Hidden Wiki. The link is onion/wiki/. Tor and Freenet are examples of darknets. markets. IP addresses, user-agent strings, and other operating system details.
New Darknet Markets
Drops are stooges who do "dirty" jobs like withdrawing money from ATMs using duplicate darknet markets onion address cards, registering a legal entity in their own name, receiving and forwarding mail items, and other activities. In this study, we address these questions by analysing a new, large, and up-to-date dataset. Telegram, the supposedly secure messaging app, has over 100 million users. Europol has organised courses on the forensics of payment card fraud. Here you can buy or sell almost anything, including drugs, software, and forgeries. The idea of Satanic ritual abuse, a bundling of everything awful in the psychological shadows, is not new. To protest against DDOS attacks, up-to-date link addresses to access the most popular dark market story available. They’re used by over 2,000 organisations across 43 different countries to understand the environmental impacts of cultural buildings, offices, outdoor events, tours and productions. Dust is a residual byproduct of trading and transacting with cryptocurrencies, and represents such small denominations of currency that it retains minimal monetary value.
It is important to note that the vast majority of Tor’s users are not necessarily accessing the Dark Web for illegal purposes. There are scams aplenty out there on the internet, and I’ve already had fun investigating some. I didn’t notice any increase in loading time compared to regular web browsing, but I was impressed that ExpressVPN maintained fast speeds even on.